
Understanding Sarcoidosis: An In-Depth Guide
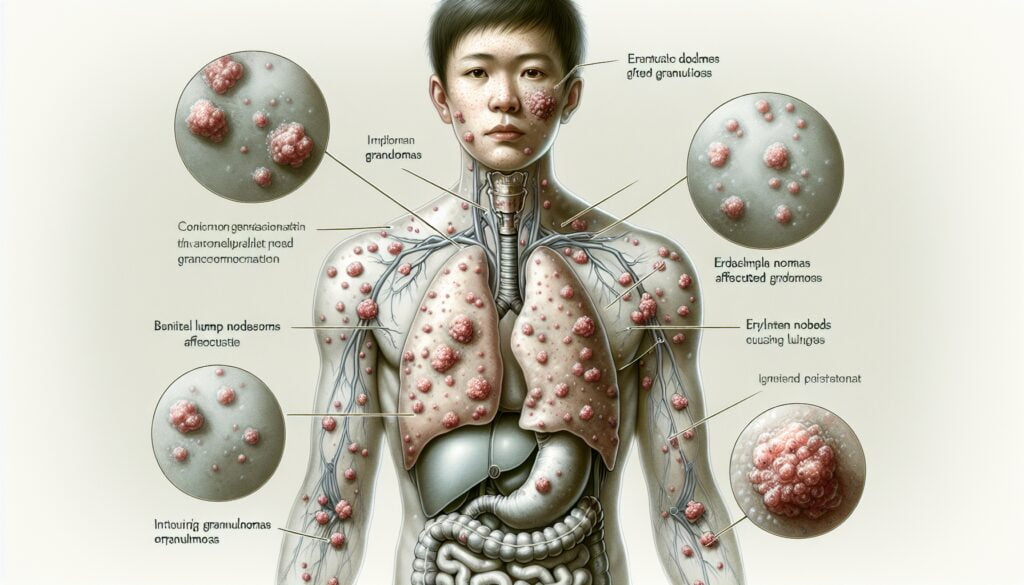
Sarcoidosis is a complex multi-system inflammatory disease that predominantly affects the lungs, but can also involve the lymph nodes, skin, eyes, and heart. This condition is characterized by the formation of granulomas—clumps of inflammatory cells—which can alter the normal structure and possibly the function of the affected organs.
The exact causes of sarcoidosis remain a mystery, but it's believed to arise from a combination of genetic predisposition and environmental triggers. Understanding sarcoidosis is crucial for those affected by it, as early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can significantly improve the quality of life and prognosis.
What is sarcoidosis?
Sarcoidosis is an enigmatic condition where tiny clumps of inflammatory cells (granulomas) form in various parts of the body, most commonly the lungs and lymph nodes. These granulomas can disrupt normal organ function and lead to a variety of symptoms. Although the pathogenesis of sarcoidosis is not fully understood, it is believed to involve an abnormal immune response to an unknown trigger.
Despite being classified as a rare disease, sarcoidosis can affect individuals worldwide, with a higher prevalence reported in Northern European and African-American populations. The disease can affect people of any age, but it typically presents in adults between the ages of 20 and 40.
The varying presentations of the disease can make it a chameleon of sorts, mimicking other conditions and making diagnosis a challenge. While it can be self-limiting in some cases, sarcoidosis can become chronic and may require long-term management.
Symptoms of sarcoidosis
The symptoms of sarcoidosis can be widely varied, as the disease can affect almost any organ system. Commonly, patients may experience cough, fatigue, shortness of breath, and chest pain. Skin manifestations like lupus pernio, erythema nodosum, and subcutaneous nodules can occur.
Other signs can include eye inflammation, leading to symptoms such as blurred vision or dry eyes. Neurological involvement might present as headaches, seizures, or weakness. If the heart is affected, individuals may experience arrhythmias or other cardiac issues.
It's worth noting that in some cases, sarcoidosis can be asymptomatic and only discovered incidentally through imaging tests for other conditions.
For a comprehensive understanding, symptoms of sarcoidosis can be organized in the following way:
- Lungs: Persistent cough, wheezing, chest discomfort
- Skin: Lesions, rashes, or nodules
- Eyes: Redness, pain, and blurred vision
- Heart: Irregular heartbeats, palpitations
- Nervous system: Headaches, numbness, or weakness
Causes of sarcoidosis
The exact causes of sarcoidosis remain unclear, but it is believed to be the result of an immune system overreaction, possibly triggered by an environmental factor in genetically predisposed individuals. Potential triggers include infections, dust, chemicals, or an abnormal reaction to the body's proteins.
Some studies suggest a link between sarcoidosis and exposure to certain materials, such as beryllium, zirconium, or talcum powder. Yet, no one trigger has been conclusively identified.
Genetics also plays a role, as evidenced by a higher incidence in certain ethnic groups and familial clustering. However, the absence of a clear pattern of inheritance indicates that multiple genes are likely to be involved.
How is sarcoidosis diagnosed?
Diagnosing sarcoidosis involves a thorough evaluation of symptoms, medical history, and a battery of tests. Key diagnostic tools include:
- Chest X-rays to detect lung involvement
- CT scans for a more detailed lung image
- Pulmonary function tests to assess lung capacity and function
- Biopsies of affected tissues to identify granulomas
- Blood tests to evaluate organ function and inflammation levels
It is crucial to rule out other conditions with similar presentations, such as tuberculosis or lymphoma, before confirming a sarcoidosis diagnosis.
Specialists from various fields, including pulmonologists, dermatologists, cardiologists, and neurologists, may be involved in the diagnostic process, reflecting the multi-system nature of the disease.
Treatment options for sarcoidosis
Although there is no cure for sarcoidosis, the treatment aims to manage symptoms and prevent organ damage. Treatment for sarcoidosis varies depending on the severity and organ involvement, and may include:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs, such as corticosteroids, to reduce inflammation and granuloma formation
- Immunosuppressive medications for patients who do not respond to steroids or have severe side effects
- Medications to manage specific symptoms like coughing or skin lesions
Lifestyle modifications, including a healthy diet, regular exercise, and avoiding exposure to lung irritants like smoke and dust, can also be beneficial. Close monitoring by health care providers is essential to adjust treatment plans as needed.
Prognosis and long-term outlook for sarcoidosis
The prognosis and long-term outlook for sarcoidosis can vary widely. Many patients experience a gradual improvement and may even achieve full remission, while others may face chronic sarcoidosis with persistent symptoms.
Factors influencing prognosis include the extent and severity of organ involvement, response to treatment, and overall health. While the disease can be life-threatening if it significantly impairs heart, lung, or nervous system function, most individuals live normal life spans with proper management.
Continual research efforts aim to improve the understanding of sarcoidosis and develop more targeted treatments to enhance outcomes for those living with the disease.
Living with sarcoidosis
Adjusting to life with sarcoidosis involves coping with the unpredictability of flare-ups and symptom management. It is vital for patients to establish a strong support network, including health care providers, friends, and family.
Regular follow-ups are necessary to monitor the condition, as sarcoidosis can sometimes worsen or lead to complications even after a period of stability. Emotional and psychological support is also essential, as chronic illnesses can have a significant impact on mental health.
Patients are encouraged to join support groups, educate themselves about the disease, and engage in advocacy to increase awareness and research funding for sarcoidosis.
What is the life expectancy with sarcoidosis?
Most individuals with sarcoidosis have a normal life expectancy. However, life expectancy can be affected if the disease causes severe damage to vital organs, such as the lungs, heart, or nervous system. Early detection and proper management are key to a favorable prognosis.
Regular monitoring and treatment adjustments can help mitigate the risks associated with sarcoidosis. It's important for patients to work closely with their healthcare team to manage their condition effectively.
How does sarcoidosis feel?
Patients with sarcoidosis often report a range of sensations depending on which organs are affected. Pulmonary involvement might feel like shortness of breath or a persistent cough. Skin symptoms can result in painful or tender lesions.
When the eyes are involved, sarcoidosis can feel like burning or itching, and vision may be affected. Regardless of the specific symptoms, many patients also experience general fatigue and discomfort.
Does sarcoidosis ever go away?
Some cases of sarcoidosis may resolve on their own without treatment, known as self-resolving sarcoidosis. However, other cases can become chronic and require ongoing management. The likelihood of remission varies by individual and can be influenced by several factors, including the severity and extent of organ involvement.
It is essential for patients to maintain regular healthcare appointments to monitor their condition and adjust treatment as necessary.
What triggers sarcoidosis flare-ups?
Identifying triggers for sarcoidosis flare-ups can be challenging, as they can vary widely among individuals. Potential triggers include stress, exposure to allergens or pollutants, infections, and abrupt changes in medication or treatment regimens.
Patients are advised to be mindful of how their lifestyle choices, such as diet and exposure to environmental irritants, may affect their condition and to communicate any concerns with their healthcare team.
Understanding sarcoidosis is essential for those diagnosed with the disease, as it equips them with the knowledge to navigate their treatment journey and advocate for their health. The complexity of sarcoidosis means that multidisciplinary care and personalized treatment plans are crucial for the best possible outcomes.






Leave a Reply