
What to know about seborrheic dermatitis: causes, symptoms, and treatment
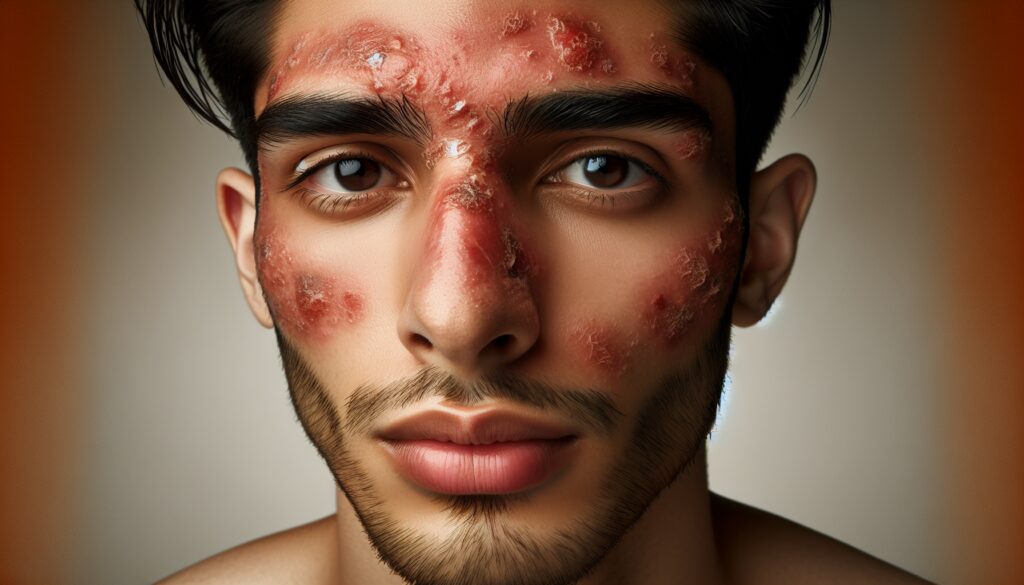
Seborrheic dermatitis is a common, chronic skin condition that primarily affects the scalp, but can also appear on other oily parts of the body such as the face, chest, and back. It is characterized by red, scaly, itchy, and flaky skin. Understanding this condition is key to managing and treating it effectively.
What Is Seborrheic Dermatitis?
Seborrheic dermatitis is a type of eczema linked to an overproduction of oil in the skin and the presence of a yeast called Malassezia. While it can resemble other skin conditions, it is known for its distinct symptoms and areas of the body it affects.
Despite being a chronic condition, seborrheic dermatitis tends to have periods of flare-ups followed by times when the symptoms may subside. Its exact cause is still not fully understood, but certain genetic and environmental factors are believed to play a role.
The condition is not contagious and can be managed with proper treatment, which often involves a combination of over-the-counter and prescription remedies.
What Causes Seborrheic Dermatitis?
Several factors may contribute to the development of seborrheic dermatitis, including:
- Genetic predisposition may influence its occurrence.
- An overproduction of skin oil (sebum) in certain areas of the body.
- The presence of the Malassezia yeast on the skin, which may provoke an inflammatory response leading to symptoms.
Other contributing factors include stress, cold and dry weather, and overall health status, which can affect the frequency and severity of flare-ups.
Additionally, certain medical conditions and medications can increase the susceptibility to developing seborrheic dermatitis.
What Are the Symptoms of Seborrheic Dermatitis?
Symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis can vary greatly from person to person but commonly include:
- Itchy, red skin in affected areas.
- White or yellowish, oily scaly patches on the scalp and other oily areas.
- Dandruff or flaky skin in the hair or on clothing.
If symptoms are present on other parts of the body, they may manifest as scaly patches or red skin in and around the ears, on the eyelids, or in skin folds.
Recognizing these symptoms early on can help with managing the condition and preventing complications such as further infection.
How Is Seborrheic Dermatitis Diagnosed?
Diagnosis of seborrheic dermatitis usually involves a physical examination of the skin. A healthcare provider may look for the telltale signs and patterns that characterize the condition. In some cases, a biopsy or a skin scraping may be performed to rule out other skin disorders.
Understanding your medical history can also help in the diagnosis, as seborrheic dermatitis can be associated with other conditions such as Parkinson's disease and HIV/AIDS.
Once diagnosed, a treatment plan can be tailored to your specific needs, which may involve a combination of medicinal and home care strategies.
Treatments for Seborrheic Dermatitis
Treatment for seborrheic dermatitis aims to reduce the inflammation and scale production that characterizes the condition. Common treatments include:
- Antifungal shampoos and creams to reduce the presence of Malassezia yeast.
- Topical corticosteroids to minimize inflammation and itching.
- Medicated shampoos containing ingredients like coal tar, salicylic acid, or ketoconazole.
- For severe cases, phototherapy or systemic treatment may be recommended.
Working with healthcare professionals is crucial in identifying the most effective treatment options, which often require regular monitoring and adjustments.
Seborrheic Dermatitis Self-Care Tips
Managing seborrheic dermatitis often involves self-care measures such as:
- Regularly washing the scalp with a gentle shampoo to reduce oiliness and build-up.
- Avoiding harsh hair products that can irritate the skin and exacerbate symptoms.
- Applying natural oils like coconut or tea tree oil, which may help soothe the skin and reduce flakiness.
Identifying and avoiding triggers, such as stress or certain foods, can also make a significant difference in the frequency and severity of flare-ups.
Creating a routine that includes gentle skin care and stress management techniques can help maintain skin health and prevent worsening of symptoms.
Frequently Asked Questions on Seborrheic Dermatitis
What Not to Do When You Have Seborrheic Dermatitis?
Avoiding certain actions can help prevent aggravating seborrheic dermatitis:
- Do not scratch affected areas, as this can lead to further irritation or infection.
- Avoid using harsh soaps and shampoos that strip the skin of its natural oils.
- Resist the temptation to pick at flakes or scales, which can also cause irritation.
Understanding your skin's needs and avoiding these actions can help manage symptoms effectively.
What Triggers Seborrheic Dermatitis?
Common triggers for seborrheic dermatitis include:
- Stress, which can worsen symptoms.
- Weather changes, particularly cold, dry conditions.
- Using alcohol-based skincare products that can irritate sensitive skin.
Identifying personal triggers is a key step in managing the condition and reducing flare-ups.
What Happens If Seborrheic Dermatitis Is Left Untreated?
If left untreated, seborrheic dermatitis can lead to more severe symptoms and skin infections. Chronic inflammation can also cause hair loss in affected areas of the scalp.
Seeking treatment and managing the condition is essential for maintaining skin health and avoiding complications.
What Can Be Mistaken for Seborrheic Dermatitis?
Several conditions may resemble seborrheic dermatitis, including:
- Psoriasis, which presents with similar scaly patches.
- Atopic dermatitis (eczema), known for its intense itchiness.
- Rosacea, which causes redness and flushing.
Distinguishing between these conditions requires a professional diagnosis, as treatments can vary significantly.
To learn more about managing seborrheic dermatitis, watch this informative video:
Living with seborrheic dermatitis can be challenging, but with the right knowledge and tools, it can be managed effectively. Keeping informed about the condition, its triggers, and treatment options is essential for anyone affected by this chronic skin disorder.






Leave a Reply